- Canada
-
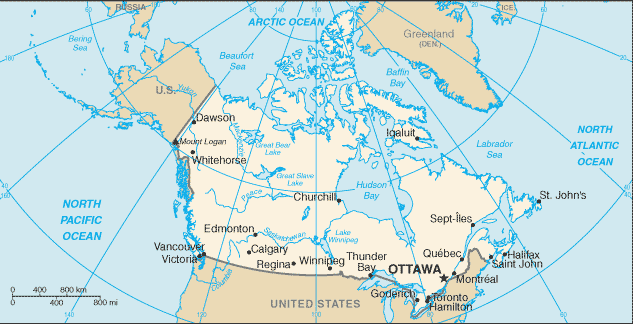 Introduction ::CanadaBackground:A land of vast distances and rich natural resources, Canada became a self-governing dominion in 1867 while retaining ties to the British crown. Economically and technologically, the nation has developed in parallel with the US, its neighbor to the south across the world's longest unfortified border. Canada faces the political challenges of meeting public demands for quality improvements in health care, education, social services, and economic competitiveness, as well as responding to the particular concerns of predominantly francophone Quebec. Canada also aims to develop its diverse energy resources while maintaining its commitment to the environment.Geography ::CanadaLocation:Northern North America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean on the east, North Pacific Ocean on the west, and the Arctic Ocean on the north, north of the conterminous USGeographic coordinates:60 00 N, 95 00 WArea:total: 9,984,670 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 2land: 9,093,507 sq kmwater: 891,163 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than the USLand boundaries:total: 8,893 kmborder countries: US 8,893 km (includes 2,477 km with Alaska)note: Canada is the World's largest country that borders only one countryCoastline:202,080 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:varies from temperate in south to subarctic and arctic in northTerrain:mostly plains with mountains in west and lowlands in southeastElevation extremes:lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Mount Logan 5,959 mNatural resources:iron ore, nickel, zinc, copper, gold, lead, rare earth elements, molybdenum, potash, diamonds, silver, fish, timber, wildlife, coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydropowerLand use:arable land: 4.3%permanent crops: 0.49%other: 95.2% (2011)Irrigated land:8,699 sq km (2004)Total renewable water resources:2,902 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 42.2 cu km/yr (20%/70%/10%)per capita: 1,589 cu m/yr (2010)Natural hazards:continuous permafrost in north is a serious obstacle to development; cyclonic storms form east of the Rocky Mountains, a result of the mixing of air masses from the Arctic, Pacific, and North American interior, and produce most of the country's rain and snow east of the mountainsvolcanism: the vast majority of volcanoes in Western Canada's Coast Mountains remain dormantEnvironment - current issues:air pollution and resulting acid rain severely affecting lakes and damaging forests; metal smelting, coal-burning utilities, and vehicle emissions impacting on agricultural and forest productivity; ocean waters becoming contaminated due to agricultural, industrial, mining, and forestry activitiesEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:second-largest country in world (after Russia); strategic location between Russia and US via north polar route; approximately 90% of the population is concentrated within 160 km of the US border; Canada has more fresh water than any other country and almost 9% of Canadian territory is water; Canada has at least 2 million and possibly over 3 million lakes - that is more than all other countries combinedPeople and Society ::CanadaNationality:noun: Canadian(s)adjective: CanadianEthnic groups:British Isles origin 28%, French origin 23%, other European 15%, Amerindian 2%, other, mostly Asian, African, Arab 6%, mixed background 26%Languages:English (official) 58.8%, French (official) 21.6%, other 19.6% (2006 Census)Religions:Roman Catholic 42.6%, Protestant 23.3% (United Church 9.5%, Anglican 6.8%, Baptist 2.4%, Lutheran 2%), other Christian 4.4%, Muslim 1.9%, other and unspecified 11.8%, none 16% (2001 census)Population:34,568,211 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Age structure:0-14 years: 15.5% (male 2,753,263/female 2,617,600)15-24 years: 12.9% (male 2,285,268/female 2,160,005)25-54 years: 41.4% (male 7,253,587/female 7,067,997)55-64 years: 13.3% (male 2,285,072/female 2,329,760)65 years and over: 16.8% (male 2,574,216/female 3,241,443) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 46.3 %youth dependency ratio: 24 %elderly dependency ratio: 22.2 %potential support ratio: 4.5 (2013)Median age:total: 41.5 yearsmale: 40.2 yearsfemale: 42.7 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.77% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Birth rate:10.28 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Death rate:8.2 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Net migration rate:5.65 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Urbanization:urban population: 81% of total population (2010)rate of urbanization: 1.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:Toronto 5.377 million; Montreal 3.75 million; Vancouver 2.197 million; OTTAWA (capital) 1.208 million; Calgary 1.16 million (2011)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.03 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:27.6 (2007 est.)Maternal mortality rate:12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 148Infant mortality rate:total: 4.78 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 182male: 5.11 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 4.43 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 81.57 yearscountry comparison to the world: 13male: 78.98 yearsfemale: 84.31 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.59 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Contraceptive prevalence rate:74%note: percent of women aged 18-44 (2002)Health expenditures:11.3% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 15Physicians density:1.91 physicians/1,000 population (2006)Hospital bed density:3.2 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.3% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 80HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:68,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 49HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 80Obesity - adult prevalence rate:26.2% (2008)country comparison to the world: 48Education expenditures:5% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 78Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99%male: 99%female: 99% (2003 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 17 yearsfemale: 17 years (2004)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 14.1%country comparison to the world: 92male: 15.9%female: 12.3% (2011)Government ::CanadaCountry name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: CanadaGovernment type:a parliamentary democracy, a federation, and a constitutional monarchyCapital:name: Ottawageographic coordinates: 45 25 N, 75 42 Wtime difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in Novembernote: Canada is divided into six time zonesAdministrative divisions:10 provinces and 3 territories*; Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Northwest Territories*, Nova Scotia, Nunavut*, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Yukon*Independence:1 July 1867 (union of British North American colonies); 11 December 1931 (recognized by UK per Statute of Westminster)National holiday:Canada Day, 1 July (1867)Constitution:made up of unwritten and written acts, customs, judicial decisions, and traditions; the written part of the constitution consists of the Constitution Act of 29 March 1867, which created a federation of four provinces, and the Constitution Act of 17 April 1982, which transferred formal control over the constitution from Britain to Canada, and added a Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms as well as procedures for constitutional amendmentsLegal system:common law system except in Quebec where civil law based on the French civil code prevailsInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:head of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General David JOHNSTON (since 1 October 2010)head of government: Prime Minister Stephen Joseph HARPER (since 6 February 2006)cabinet: Federal Ministry chosen by the prime minister usually from among the members of his own party sitting in Parliament(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister for a five-year term; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition in the House of Commons generally designated prime minister by the governor generalLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate or Senat (105 seats; members appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister and serve until 75 years of age) and the House of Commons or Chambre des Communes (308 seats; members elected by direct, popular vote to serve a maximum of four-year terms)elections: House of Commons - last held on 2 May 2011 (next to be held no later than 19 October 2015)election results: House of Commons - percent of vote by party - Conservative Party 39.6%, NDP 30.6%, Liberal Party 18.9%, Bloc Quebecois 6%, Greens 3.9%; seats by party - Conservative Party 166, NDP 103, Liberal Party 34, Bloc Quebecois 4, Greens 1Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of Canada (consists of the chief justice and 8 judges)note - in 1949, Canada finally abolished all appeals beyond its Supreme Court to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)judge selection and term of office: chief justice and judges appointed by the prime minister in council; all judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 75subordinate courts: federal level: Federal Court of Appeal; Federal Court; Tax Court; federal administrative tribunals; courts martial; provincial/territorial: provincial superior, appeals, first instance, and specialized courts; in 1999, the Nunavut Court - a circuit court with the power of a superior court and the territorial courts - was established to serve isolated settlementsPolitical parties and leaders:Bloc Quebecois [Daniel PAILLE]Conservative Party of Canada [Stephen HARPER]Green Party [Elizabeth MAY]Liberal Party [Robert RAE (interim)]New Democratic Party or NDP [Thomas MULCAIR]Political pressure groups and leaders:other: agricultural sector; automobile industry; business groups; chemical industry; commercial banks; communications sector; energy industry; environmentalists; public administration groups; steel industry; trade unionsInternational organization participation:ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, Arctic Council, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, C, CD, CDB, CE (observer), EAPC, EBRD, EITI (implementing country), FAO, FATF, G-20, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAFTA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS, OECD, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Gary DOERchancery: 501 Pennsylvania Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20001telephone: [1] (202) 682-1740FAX: [1] (202) 682-7726consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Buffalo, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Detroit, Los Angeles, Miami, Minneapolis, New York, San Francisco/Silicon Valley, Seattleconsulate(s): Anchorage (AK), Houston, Palo Alto (CA), Philadelphia, Phoenix, Raleigh (NC), Salt Lake City, San Diego, TucsonDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador David C. JACOBSONembassy: 490 Sussex Drive, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 1G8mailing address: P. O. Box 5000, Ogdensburg, NY 13669-0430; P.O. Box 866, Station B, Ottawa, Ontario K1P 5T1telephone: [1] (613) 688-5335FAX: [1] (613) 688-3082consulate(s) general: Calgary, Halifax, Montreal, Quebec City, Toronto, Vancouver, WinnipegFlag description:two vertical bands of red (hoist and fly side, half width) with white square between them; an 11-pointed red maple leaf is centered in the white square; the maple leaf has long been a Canadian symbol; the official colors of Canada are red and whiteNational symbol(s):maple leafNational anthem:name: ""O Canada""lyrics/music: Adolphe-Basile ROUTHIER [French], Robert Stanley WEIR [English]/Calixa LAVALLEEnote: adopted 1980; originally written in 1880, ""O Canada"" served as an unofficial anthem many years before its official adoption; the anthem has French and English versions whose lyrics differ; as a Commonwealth realm, in addition to the national anthem, ""God Save the Queen"" serves as the royal anthem (see United Kingdom)Economy ::CanadaEconomy - overview:As a high-tech industrial society in the trillion-dollar class, Canada resembles the US in its market-oriented economic system, pattern of production, and affluent living standards. Since World War II, the impressive growth of the manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation from a largely rural economy into one primarily industrial and urban. The 1989 US-Canada Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and the 1994 North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (which includes Mexico) touched off a dramatic increase in trade and economic integration with the US its principal trading partner. Canada enjoys a substantial trade surplus with the US, which absorbs about three-fourths of Canadian exports each year. Canada is the US's largest foreign supplier of energy, including oil, gas, uranium, and electric power. Given its great natural resources, highly skilled labor force, and modern capital plant, Canada enjoyed solid economic growth from 1993 through 2007. Buffeted by the global economic crisis, the economy dropped into a sharp recession in the final months of 2008, and Ottawa posted its first fiscal deficit in 2009 after 12 years of surplus. Canada's major banks, however, emerged from the financial crisis of 2008-09 among the strongest in the world, owing to the financial sector's tradition of conservative lending practices and strong capitalization. Canada achieved marginal growth in 2010-12 and plans to balance the budget by 2015. In addition, the country's petroleum sector is rapidly becoming an even larger economic driver with Alberta's oil sands significantly boosting Canada's proven oil reserves, ranking the country third in the world behind Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.GDP (purchasing power parity):$1.513 trillion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 14$1.485 trillion (2011 est.)$1.448 trillion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$1.819 trillion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:1.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1422.6% (2011 est.)3.2% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$43,400 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 19$43,100 (2011 est.)$42,500 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:20.8% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7020.6% of GDP (2011 est.)19.7% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 55.8%government consumption: 21.7%investment in fixed capital: 24%investment in inventories: 0.4%exports of goods and services: 30%imports of goods and services: -32%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 1.7%industry: 28.5%services: 69.8% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:wheat, barley, oilseed, tobacco, fruits, vegetables; dairy products; fish; forest productsIndustries:transportation equipment, chemicals, processed and unprocessed minerals, food products, wood and paper products, fish products, petroleum and natural gasIndustrial production growth rate:1.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Labor force:18.89 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 2%manufacturing: 13%construction: 6%services: 76%other: 3% (2006 est.)Unemployment rate:7.3% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 817.5% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:9.4%note: this figure is the Low Income Cut-Off (LICO), a calculation that results in higher figures than found in many comparable economies; Canada does not have an official poverty line (2008)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.6%highest 10%: 24.8% (2000)Distribution of family income - Gini index:32.1 (2005)country comparison to the world: 10331.5 (1994)Budget:revenues: $682.5 billionexpenditures: $749.5 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:37.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Public debt:84.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2383.4% of GDP (2011 est.)note: figures are for gross general government debt, as opposed to net federal debt; gross general government debt includes both intragovernmental debt and the debt of public entities at the sub-national levelFiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):1.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 292.9% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:1% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1410.25% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:3% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1763% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$654.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$585 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$1.523 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13$1.404 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$3.083 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$2.836 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.907 trillion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 7$2.16 trillion (31 December 2010)$1.681 trillion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:-$59.92 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 190-$48.91 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$462.9 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13$461.4 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:motor vehicles and parts, industrial machinery, aircraft, telecommunications equipment; chemicals, plastics, fertilizers; wood pulp, timber, crude petroleum, natural gas, electricity, aluminumExports - partners:US 74.5%, China 4.3%, UK 4.1% (2012)Imports:$474.8 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11$460.4 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and equipment, motor vehicles and parts, crude oil, chemicals, electricity, durable consumer goodsImports - partners:US 50.6%, China 11%, Mexico 5.5% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$68.55 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$65.82 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$1.326 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 15$1.191 trillion (31 December 2011)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$918.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8$873.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$953.3 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$899.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Canadian dollars (CAD) per US dollar -0.9992 (2012 est.)0.9895 (2011 est.)1.0302 (2010 est.)1.1431 (2009)1.0364 (2008)Energy ::CanadaElectricity - production:580.6 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Electricity - consumption:504.8 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Electricity - exports:43.91 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Electricity - imports:18.79 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Electricity - installed generating capacity:131.5 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Electricity - from fossil fuels:28.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Electricity - from nuclear fuels:10.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:57% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Electricity - from other renewable sources:3.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Crude oil - production:3.592 million bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Crude oil - exports:1.355 million bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Crude oil - imports:791,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Crude oil - proved reserves:173.6 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Refined petroleum products - production:1.978 million bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Refined petroleum products - consumption:2.259 million bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Refined petroleum products - exports:437,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Refined petroleum products - imports:282,200 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Natural gas - production:160.1 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Natural gas - consumption:103.3 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Natural gas - exports:92.72 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Natural gas - imports:30.49 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 14Natural gas - proved reserves:1.727 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:548.8 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Communications ::CanadaTelephones - main lines in use:18.201 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 16Telephones - mobile cellular:27.387 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 37Telephone system:general assessment: excellent service provided by modern technologydomestic: domestic satellite system with about 300 earth stationsinternational: country code - 1; submarine cables provide links to the US and Europe; satellite earth stations - 7 (5 Intelsat - 4 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Pacific Ocean, and 2 Intersputnik - Atlantic Ocean region) (2011)Broadcast media:2 public TV broadcasting networks each with a large number of network affiliates; several private-commercial networks also with multiple network affiliates; overall, about 150 TV stations; multi-channel satellite and cable systems provide access to a wide range of stations including US stations; mix of public and commercial radio broadcasters with the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), the public radio broadcaster, operating 4 radio networks, Radio Canada International, and radio services to indigenous populations in the north; roughly 2,000 licensed radio stations in Canada (2008)Internet country code:.caInternet hosts:8.743 million (2012)country comparison to the world: 14Internet users:26.96 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 16Transportation ::CanadaAirports:1,467 (2013)country comparison to the world: 4Airports - with paved runways:total: 523over 3,047 m: 212,438 to 3,047 m: 191,524 to 2,437 m: 147914 to 1,523 m: 257under 914 m: 79 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 9441,524 to 2,437 m: 75914 to 1,523 m: 385under 914 m:484 (2013)Heliports:26 (2013)Pipelines:gas and liguid petroleum 100,000 km (2013)Railways:total: 46,552 kmcountry comparison to the world: 5standard gauge: 46,552 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 1,042,300 kmcountry comparison to the world: 6paved: 415,600 km (includes 17,000 km of expressways)unpaved: 626,700 km (2008)Waterways:636 km (Saint Lawrence Seaway of 3,769 km, including the Saint Lawrence River of 3,058 km, shared with United States) (2011)country comparison to the world: 78Merchant marine:total: 181country comparison to the world: 35by type: bulk carrier 62, cargo 15, carrier 1, chemical tanker 15, combination ore/oil 1, container 2, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 63, petroleum tanker 11, roll on/roll off 6foreign-owned: 19 (Estonia 1, France 1, Netherlands 1, Norway 4, Sweden 2, US 10)registered in other countries: 225 (Australia 5, Bahamas 96, Barbados 11, Cambodia 2, Cyprus 2, Honduras 1, Hong Kong 77, Liberia 2, Malta 5, Marshall Islands 8, Norway 1, Panama 6, Spain 4, Vanuatu 5) (2010)Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Halifax, Saint John (New Brunswick), Vancouverriver and lake port(s): Montreal, Quebec City, Sept-Isles (St. Lawrence); Fraser River Port (Fraser); Hamilton (Lake Ontario)oil/gas terminal(s): Lower Lakes terminaldry bulk cargo port(s): Port-Cartier (iron ore and grain),container port(s): Montreal (1,362,975), Vancouver (2,507,032)(2011)Military ::CanadaMilitary branches:Canadian Forces: Canadian Army, Royal Canadian Navy, Royal Canadian Air Force, Canada Command (homeland security) (2011)Military service age and obligation:17 years of age for voluntary male and female military service (with parental consent); 16 years of age for Reserve and Military College applicants; Canadian citizenship or permanent residence status required; maximum 34 years of age; service obligation 3-9 years (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 8,031,266females age 16-49: 7,755,550 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 6,633,472females age 16-49: 6,389,669 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 218,069female: 206,195 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.1% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Transnational Issues ::CanadaDisputes - international:managed maritime boundary disputes with the US at Dixon Entrance, Beaufort Sea, Strait of Juan de Fuca, and the Gulf of Maine including the disputed Machias Seal Island and North Rock; Canada and the United States dispute how to divide the Beaufort Sea and the status of the Northwest Passage but continue to work cooperatively to survey the Arctic continental shelf; US works closely with Canada to intensify security measures for monitoring and controlling legal and illegal movement of people, transport, and commodities across the international border; sovereignty dispute with Denmark over Hans Island in the Kennedy Channel between Ellesmere Island and Greenland; commencing the collection of technical evidence for submission to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf in support of claims for continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles from its declared baselines in the Arctic, as stipulated in Article 76, paragraph 8, of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the SeaRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 17,563 (Colombia); 16,813 (China); 13,705 (Sri Lanka); 11,605 (Pakistan); 6,798 (Haiti); 5,995 (Mexico); 5,287 (India) (2012)Illicit drugs:illicit producer of cannabis for the domestic drug market and export to US; use of hydroponics technology permits growers to plant large quantities of high-quality marijuana indoors; increasing ecstasy production, some of which is destined for the US; vulnerable to narcotics money laundering because of its mature financial services sector"
Introduction ::CanadaBackground:A land of vast distances and rich natural resources, Canada became a self-governing dominion in 1867 while retaining ties to the British crown. Economically and technologically, the nation has developed in parallel with the US, its neighbor to the south across the world's longest unfortified border. Canada faces the political challenges of meeting public demands for quality improvements in health care, education, social services, and economic competitiveness, as well as responding to the particular concerns of predominantly francophone Quebec. Canada also aims to develop its diverse energy resources while maintaining its commitment to the environment.Geography ::CanadaLocation:Northern North America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean on the east, North Pacific Ocean on the west, and the Arctic Ocean on the north, north of the conterminous USGeographic coordinates:60 00 N, 95 00 WArea:total: 9,984,670 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 2land: 9,093,507 sq kmwater: 891,163 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than the USLand boundaries:total: 8,893 kmborder countries: US 8,893 km (includes 2,477 km with Alaska)note: Canada is the World's largest country that borders only one countryCoastline:202,080 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:varies from temperate in south to subarctic and arctic in northTerrain:mostly plains with mountains in west and lowlands in southeastElevation extremes:lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Mount Logan 5,959 mNatural resources:iron ore, nickel, zinc, copper, gold, lead, rare earth elements, molybdenum, potash, diamonds, silver, fish, timber, wildlife, coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydropowerLand use:arable land: 4.3%permanent crops: 0.49%other: 95.2% (2011)Irrigated land:8,699 sq km (2004)Total renewable water resources:2,902 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 42.2 cu km/yr (20%/70%/10%)per capita: 1,589 cu m/yr (2010)Natural hazards:continuous permafrost in north is a serious obstacle to development; cyclonic storms form east of the Rocky Mountains, a result of the mixing of air masses from the Arctic, Pacific, and North American interior, and produce most of the country's rain and snow east of the mountainsvolcanism: the vast majority of volcanoes in Western Canada's Coast Mountains remain dormantEnvironment - current issues:air pollution and resulting acid rain severely affecting lakes and damaging forests; metal smelting, coal-burning utilities, and vehicle emissions impacting on agricultural and forest productivity; ocean waters becoming contaminated due to agricultural, industrial, mining, and forestry activitiesEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:second-largest country in world (after Russia); strategic location between Russia and US via north polar route; approximately 90% of the population is concentrated within 160 km of the US border; Canada has more fresh water than any other country and almost 9% of Canadian territory is water; Canada has at least 2 million and possibly over 3 million lakes - that is more than all other countries combinedPeople and Society ::CanadaNationality:noun: Canadian(s)adjective: CanadianEthnic groups:British Isles origin 28%, French origin 23%, other European 15%, Amerindian 2%, other, mostly Asian, African, Arab 6%, mixed background 26%Languages:English (official) 58.8%, French (official) 21.6%, other 19.6% (2006 Census)Religions:Roman Catholic 42.6%, Protestant 23.3% (United Church 9.5%, Anglican 6.8%, Baptist 2.4%, Lutheran 2%), other Christian 4.4%, Muslim 1.9%, other and unspecified 11.8%, none 16% (2001 census)Population:34,568,211 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Age structure:0-14 years: 15.5% (male 2,753,263/female 2,617,600)15-24 years: 12.9% (male 2,285,268/female 2,160,005)25-54 years: 41.4% (male 7,253,587/female 7,067,997)55-64 years: 13.3% (male 2,285,072/female 2,329,760)65 years and over: 16.8% (male 2,574,216/female 3,241,443) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 46.3 %youth dependency ratio: 24 %elderly dependency ratio: 22.2 %potential support ratio: 4.5 (2013)Median age:total: 41.5 yearsmale: 40.2 yearsfemale: 42.7 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.77% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Birth rate:10.28 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Death rate:8.2 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Net migration rate:5.65 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Urbanization:urban population: 81% of total population (2010)rate of urbanization: 1.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:Toronto 5.377 million; Montreal 3.75 million; Vancouver 2.197 million; OTTAWA (capital) 1.208 million; Calgary 1.16 million (2011)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.03 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:27.6 (2007 est.)Maternal mortality rate:12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 148Infant mortality rate:total: 4.78 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 182male: 5.11 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 4.43 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 81.57 yearscountry comparison to the world: 13male: 78.98 yearsfemale: 84.31 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.59 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Contraceptive prevalence rate:74%note: percent of women aged 18-44 (2002)Health expenditures:11.3% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 15Physicians density:1.91 physicians/1,000 population (2006)Hospital bed density:3.2 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.3% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 80HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:68,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 49HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 80Obesity - adult prevalence rate:26.2% (2008)country comparison to the world: 48Education expenditures:5% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 78Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99%male: 99%female: 99% (2003 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 17 yearsfemale: 17 years (2004)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 14.1%country comparison to the world: 92male: 15.9%female: 12.3% (2011)Government ::CanadaCountry name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: CanadaGovernment type:a parliamentary democracy, a federation, and a constitutional monarchyCapital:name: Ottawageographic coordinates: 45 25 N, 75 42 Wtime difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in Novembernote: Canada is divided into six time zonesAdministrative divisions:10 provinces and 3 territories*; Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Northwest Territories*, Nova Scotia, Nunavut*, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Yukon*Independence:1 July 1867 (union of British North American colonies); 11 December 1931 (recognized by UK per Statute of Westminster)National holiday:Canada Day, 1 July (1867)Constitution:made up of unwritten and written acts, customs, judicial decisions, and traditions; the written part of the constitution consists of the Constitution Act of 29 March 1867, which created a federation of four provinces, and the Constitution Act of 17 April 1982, which transferred formal control over the constitution from Britain to Canada, and added a Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms as well as procedures for constitutional amendmentsLegal system:common law system except in Quebec where civil law based on the French civil code prevailsInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:head of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General David JOHNSTON (since 1 October 2010)head of government: Prime Minister Stephen Joseph HARPER (since 6 February 2006)cabinet: Federal Ministry chosen by the prime minister usually from among the members of his own party sitting in Parliament(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister for a five-year term; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of the majority coalition in the House of Commons generally designated prime minister by the governor generalLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate or Senat (105 seats; members appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister and serve until 75 years of age) and the House of Commons or Chambre des Communes (308 seats; members elected by direct, popular vote to serve a maximum of four-year terms)elections: House of Commons - last held on 2 May 2011 (next to be held no later than 19 October 2015)election results: House of Commons - percent of vote by party - Conservative Party 39.6%, NDP 30.6%, Liberal Party 18.9%, Bloc Quebecois 6%, Greens 3.9%; seats by party - Conservative Party 166, NDP 103, Liberal Party 34, Bloc Quebecois 4, Greens 1Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of Canada (consists of the chief justice and 8 judges)note - in 1949, Canada finally abolished all appeals beyond its Supreme Court to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London)judge selection and term of office: chief justice and judges appointed by the prime minister in council; all judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 75subordinate courts: federal level: Federal Court of Appeal; Federal Court; Tax Court; federal administrative tribunals; courts martial; provincial/territorial: provincial superior, appeals, first instance, and specialized courts; in 1999, the Nunavut Court - a circuit court with the power of a superior court and the territorial courts - was established to serve isolated settlementsPolitical parties and leaders:Bloc Quebecois [Daniel PAILLE]Conservative Party of Canada [Stephen HARPER]Green Party [Elizabeth MAY]Liberal Party [Robert RAE (interim)]New Democratic Party or NDP [Thomas MULCAIR]Political pressure groups and leaders:other: agricultural sector; automobile industry; business groups; chemical industry; commercial banks; communications sector; energy industry; environmentalists; public administration groups; steel industry; trade unionsInternational organization participation:ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, Arctic Council, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, C, CD, CDB, CE (observer), EAPC, EBRD, EITI (implementing country), FAO, FATF, G-20, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAFTA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS, OECD, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Gary DOERchancery: 501 Pennsylvania Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20001telephone: [1] (202) 682-1740FAX: [1] (202) 682-7726consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Buffalo, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Detroit, Los Angeles, Miami, Minneapolis, New York, San Francisco/Silicon Valley, Seattleconsulate(s): Anchorage (AK), Houston, Palo Alto (CA), Philadelphia, Phoenix, Raleigh (NC), Salt Lake City, San Diego, TucsonDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador David C. JACOBSONembassy: 490 Sussex Drive, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 1G8mailing address: P. O. Box 5000, Ogdensburg, NY 13669-0430; P.O. Box 866, Station B, Ottawa, Ontario K1P 5T1telephone: [1] (613) 688-5335FAX: [1] (613) 688-3082consulate(s) general: Calgary, Halifax, Montreal, Quebec City, Toronto, Vancouver, WinnipegFlag description:two vertical bands of red (hoist and fly side, half width) with white square between them; an 11-pointed red maple leaf is centered in the white square; the maple leaf has long been a Canadian symbol; the official colors of Canada are red and whiteNational symbol(s):maple leafNational anthem:name: ""O Canada""lyrics/music: Adolphe-Basile ROUTHIER [French], Robert Stanley WEIR [English]/Calixa LAVALLEEnote: adopted 1980; originally written in 1880, ""O Canada"" served as an unofficial anthem many years before its official adoption; the anthem has French and English versions whose lyrics differ; as a Commonwealth realm, in addition to the national anthem, ""God Save the Queen"" serves as the royal anthem (see United Kingdom)Economy ::CanadaEconomy - overview:As a high-tech industrial society in the trillion-dollar class, Canada resembles the US in its market-oriented economic system, pattern of production, and affluent living standards. Since World War II, the impressive growth of the manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation from a largely rural economy into one primarily industrial and urban. The 1989 US-Canada Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and the 1994 North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (which includes Mexico) touched off a dramatic increase in trade and economic integration with the US its principal trading partner. Canada enjoys a substantial trade surplus with the US, which absorbs about three-fourths of Canadian exports each year. Canada is the US's largest foreign supplier of energy, including oil, gas, uranium, and electric power. Given its great natural resources, highly skilled labor force, and modern capital plant, Canada enjoyed solid economic growth from 1993 through 2007. Buffeted by the global economic crisis, the economy dropped into a sharp recession in the final months of 2008, and Ottawa posted its first fiscal deficit in 2009 after 12 years of surplus. Canada's major banks, however, emerged from the financial crisis of 2008-09 among the strongest in the world, owing to the financial sector's tradition of conservative lending practices and strong capitalization. Canada achieved marginal growth in 2010-12 and plans to balance the budget by 2015. In addition, the country's petroleum sector is rapidly becoming an even larger economic driver with Alberta's oil sands significantly boosting Canada's proven oil reserves, ranking the country third in the world behind Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.GDP (purchasing power parity):$1.513 trillion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 14$1.485 trillion (2011 est.)$1.448 trillion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$1.819 trillion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:1.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1422.6% (2011 est.)3.2% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$43,400 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 19$43,100 (2011 est.)$42,500 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:20.8% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 7020.6% of GDP (2011 est.)19.7% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 55.8%government consumption: 21.7%investment in fixed capital: 24%investment in inventories: 0.4%exports of goods and services: 30%imports of goods and services: -32%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 1.7%industry: 28.5%services: 69.8% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:wheat, barley, oilseed, tobacco, fruits, vegetables; dairy products; fish; forest productsIndustries:transportation equipment, chemicals, processed and unprocessed minerals, food products, wood and paper products, fish products, petroleum and natural gasIndustrial production growth rate:1.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 103Labor force:18.89 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 2%manufacturing: 13%construction: 6%services: 76%other: 3% (2006 est.)Unemployment rate:7.3% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 817.5% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:9.4%note: this figure is the Low Income Cut-Off (LICO), a calculation that results in higher figures than found in many comparable economies; Canada does not have an official poverty line (2008)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.6%highest 10%: 24.8% (2000)Distribution of family income - Gini index:32.1 (2005)country comparison to the world: 10331.5 (1994)Budget:revenues: $682.5 billionexpenditures: $749.5 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:37.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Public debt:84.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2383.4% of GDP (2011 est.)note: figures are for gross general government debt, as opposed to net federal debt; gross general government debt includes both intragovernmental debt and the debt of public entities at the sub-national levelFiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):1.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 292.9% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:1% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1410.25% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:3% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1763% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$654.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$585 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$1.523 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13$1.404 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$3.083 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$2.836 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.907 trillion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 7$2.16 trillion (31 December 2010)$1.681 trillion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:-$59.92 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 190-$48.91 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$462.9 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 13$461.4 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:motor vehicles and parts, industrial machinery, aircraft, telecommunications equipment; chemicals, plastics, fertilizers; wood pulp, timber, crude petroleum, natural gas, electricity, aluminumExports - partners:US 74.5%, China 4.3%, UK 4.1% (2012)Imports:$474.8 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 11$460.4 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and equipment, motor vehicles and parts, crude oil, chemicals, electricity, durable consumer goodsImports - partners:US 50.6%, China 11%, Mexico 5.5% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$68.55 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$65.82 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$1.326 trillion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 15$1.191 trillion (31 December 2011)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$918.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8$873.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$953.3 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9$899.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Canadian dollars (CAD) per US dollar -0.9992 (2012 est.)0.9895 (2011 est.)1.0302 (2010 est.)1.1431 (2009)1.0364 (2008)Energy ::CanadaElectricity - production:580.6 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Electricity - consumption:504.8 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Electricity - exports:43.91 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Electricity - imports:18.79 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Electricity - installed generating capacity:131.5 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Electricity - from fossil fuels:28.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Electricity - from nuclear fuels:10.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:57% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Electricity - from other renewable sources:3.9% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Crude oil - production:3.592 million bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Crude oil - exports:1.355 million bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Crude oil - imports:791,100 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Crude oil - proved reserves:173.6 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Refined petroleum products - production:1.978 million bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Refined petroleum products - consumption:2.259 million bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Refined petroleum products - exports:437,300 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Refined petroleum products - imports:282,200 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Natural gas - production:160.1 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Natural gas - consumption:103.3 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 7Natural gas - exports:92.72 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Natural gas - imports:30.49 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 14Natural gas - proved reserves:1.727 trillion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 21Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:548.8 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Communications ::CanadaTelephones - main lines in use:18.201 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 16Telephones - mobile cellular:27.387 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 37Telephone system:general assessment: excellent service provided by modern technologydomestic: domestic satellite system with about 300 earth stationsinternational: country code - 1; submarine cables provide links to the US and Europe; satellite earth stations - 7 (5 Intelsat - 4 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Pacific Ocean, and 2 Intersputnik - Atlantic Ocean region) (2011)Broadcast media:2 public TV broadcasting networks each with a large number of network affiliates; several private-commercial networks also with multiple network affiliates; overall, about 150 TV stations; multi-channel satellite and cable systems provide access to a wide range of stations including US stations; mix of public and commercial radio broadcasters with the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), the public radio broadcaster, operating 4 radio networks, Radio Canada International, and radio services to indigenous populations in the north; roughly 2,000 licensed radio stations in Canada (2008)Internet country code:.caInternet hosts:8.743 million (2012)country comparison to the world: 14Internet users:26.96 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 16Transportation ::CanadaAirports:1,467 (2013)country comparison to the world: 4Airports - with paved runways:total: 523over 3,047 m: 212,438 to 3,047 m: 191,524 to 2,437 m: 147914 to 1,523 m: 257under 914 m: 79 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 9441,524 to 2,437 m: 75914 to 1,523 m: 385under 914 m:484 (2013)Heliports:26 (2013)Pipelines:gas and liguid petroleum 100,000 km (2013)Railways:total: 46,552 kmcountry comparison to the world: 5standard gauge: 46,552 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)Roadways:total: 1,042,300 kmcountry comparison to the world: 6paved: 415,600 km (includes 17,000 km of expressways)unpaved: 626,700 km (2008)Waterways:636 km (Saint Lawrence Seaway of 3,769 km, including the Saint Lawrence River of 3,058 km, shared with United States) (2011)country comparison to the world: 78Merchant marine:total: 181country comparison to the world: 35by type: bulk carrier 62, cargo 15, carrier 1, chemical tanker 15, combination ore/oil 1, container 2, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 63, petroleum tanker 11, roll on/roll off 6foreign-owned: 19 (Estonia 1, France 1, Netherlands 1, Norway 4, Sweden 2, US 10)registered in other countries: 225 (Australia 5, Bahamas 96, Barbados 11, Cambodia 2, Cyprus 2, Honduras 1, Hong Kong 77, Liberia 2, Malta 5, Marshall Islands 8, Norway 1, Panama 6, Spain 4, Vanuatu 5) (2010)Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Halifax, Saint John (New Brunswick), Vancouverriver and lake port(s): Montreal, Quebec City, Sept-Isles (St. Lawrence); Fraser River Port (Fraser); Hamilton (Lake Ontario)oil/gas terminal(s): Lower Lakes terminaldry bulk cargo port(s): Port-Cartier (iron ore and grain),container port(s): Montreal (1,362,975), Vancouver (2,507,032)(2011)Military ::CanadaMilitary branches:Canadian Forces: Canadian Army, Royal Canadian Navy, Royal Canadian Air Force, Canada Command (homeland security) (2011)Military service age and obligation:17 years of age for voluntary male and female military service (with parental consent); 16 years of age for Reserve and Military College applicants; Canadian citizenship or permanent residence status required; maximum 34 years of age; service obligation 3-9 years (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 8,031,266females age 16-49: 7,755,550 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 6,633,472females age 16-49: 6,389,669 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 218,069female: 206,195 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.1% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Transnational Issues ::CanadaDisputes - international:managed maritime boundary disputes with the US at Dixon Entrance, Beaufort Sea, Strait of Juan de Fuca, and the Gulf of Maine including the disputed Machias Seal Island and North Rock; Canada and the United States dispute how to divide the Beaufort Sea and the status of the Northwest Passage but continue to work cooperatively to survey the Arctic continental shelf; US works closely with Canada to intensify security measures for monitoring and controlling legal and illegal movement of people, transport, and commodities across the international border; sovereignty dispute with Denmark over Hans Island in the Kennedy Channel between Ellesmere Island and Greenland; commencing the collection of technical evidence for submission to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf in support of claims for continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles from its declared baselines in the Arctic, as stipulated in Article 76, paragraph 8, of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the SeaRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 17,563 (Colombia); 16,813 (China); 13,705 (Sri Lanka); 11,605 (Pakistan); 6,798 (Haiti); 5,995 (Mexico); 5,287 (India) (2012)Illicit drugs:illicit producer of cannabis for the domestic drug market and export to US; use of hydroponics technology permits growers to plant large quantities of high-quality marijuana indoors; increasing ecstasy production, some of which is destined for the US; vulnerable to narcotics money laundering because of its mature financial services sector"
The World Factbook. 2014.
